The most useful tool for a software developer, other than the brain, is an integrated development environment (IDE). You may have used IDEs in your classes, such as IDLE (which is bundled with Python), PyCharm, IntelliJ, Visual Studio, or XCode. IDEs usually have the following capabilities at a minimum:
- Text editing for writing source code
- Running the code
- Debugging (more on this in the future)
- Browsing files
- Searching through files
- Navigating through code structures easily
Most IDEs have many more capabilities. Software developers develop a preference for an IDE based on its capabilities, its ease-of-use, and the programming languages it supports.
In this class, we will use PyCharm, an IDE published by JetBrains. It has many handy features to support Python programming.
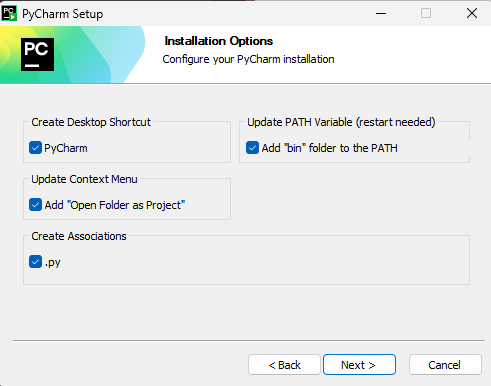
PyCharm works on Windows, Mac, and graphical Linux-based operating systems. If you are using Windows, we want to run it from our Linux environment
Choose the section corresponding to your Linux environment for instructions on installing PyCharm.