Flask server app
Intro
The Python web application above is written using the Flask framework. Flask is used by companies including Netflix, Uber, and LinkedIn to create web applications. It is installed as a Python library with the pip tool.
Webapp setup
Deploying this Flask web application to ada is your Assignment #7. Follow these steps to check out and run the project on your computer:
- Accept the GitHub Classroom assignment #7: https://classroom.github.com/a/wbeITctx. This is an individual assignment.
- Clone the repo to your your local computer. This should create a project directory called
assn7-<your_name>or something similar. - Using your Terminal,
cdinto the project directory. - Open Visual Studio Code in the working directory with
code .. It is essential that yourassn7-<your-name>/directory is the top-level of Visual Studio Code. - In the menu bar, select View → Command Palette
- Search for “environment” and select Python: Create Environment…
- Select Venv
- Select a recent Python version.
- On “Select dependencies to install”, check the box next to
requirements.txt. Click “Okay”.
It may take a minute. Visual Studio Code will create a copy of Python in the directory in the .venv/ subdirectory. This is considered best practice in Python development when you need to install libraries, like Flask, so that you do not “pollute” the system Python directory with many libraries that are not needed for all your programs.
Project structure
You will see several files in the project folder:
app.py: This is the main Python file that defines the Flask application. It specifies what types of requests to respond to. It calls the other files to handle the logic. Think of it as the user interface of the application.quizzer.py: a plain Python file that has some functions related to quiz questions and answers. This functions are called byapp.py.questions.py: contains a Python class definition for aMultipleChoiceQuestionand initializes a list of QUESTIONS the app serves.test_quizzer.py: unit tests forquizzer.py. You can runpytestin the Terminal to try them.templates/: website files go in here to be sent to a browser. For now, there is onlyindex.html, whichapp.pysends back to clients that browser to the server’s home page.- Other things:
.venv/: the Python virtual environment used to run the app. Ignore this..gitignore: tells Git to ignore specific files.requirements.txt: tells the virtual environment whichpiplibraries are needed to run the project.
Running the webapp
We need to run the Flask web application from Visual Studio Code’s integrated terminal.
Note: Flask will only run with the “virtual environment” in .venv/ active. Visual Studio Code will activate it for you automatically. If you want to run from your system Terminal, you will need to run source .venv/bin/activate first from your project directory.
Run flask --app app run --debug to start the Flask webapp. You should see output similar to the following in your Terminal: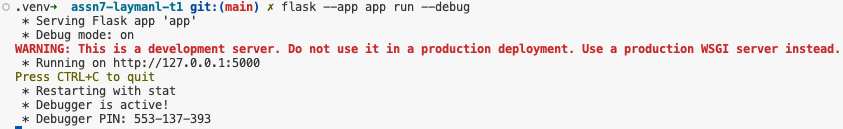
You may be prompted by your OS to allow connections. You do not need to allow external connections for it to work.
Open a web browser to http://127.0.0.1:5000
You should see the Welcome Page: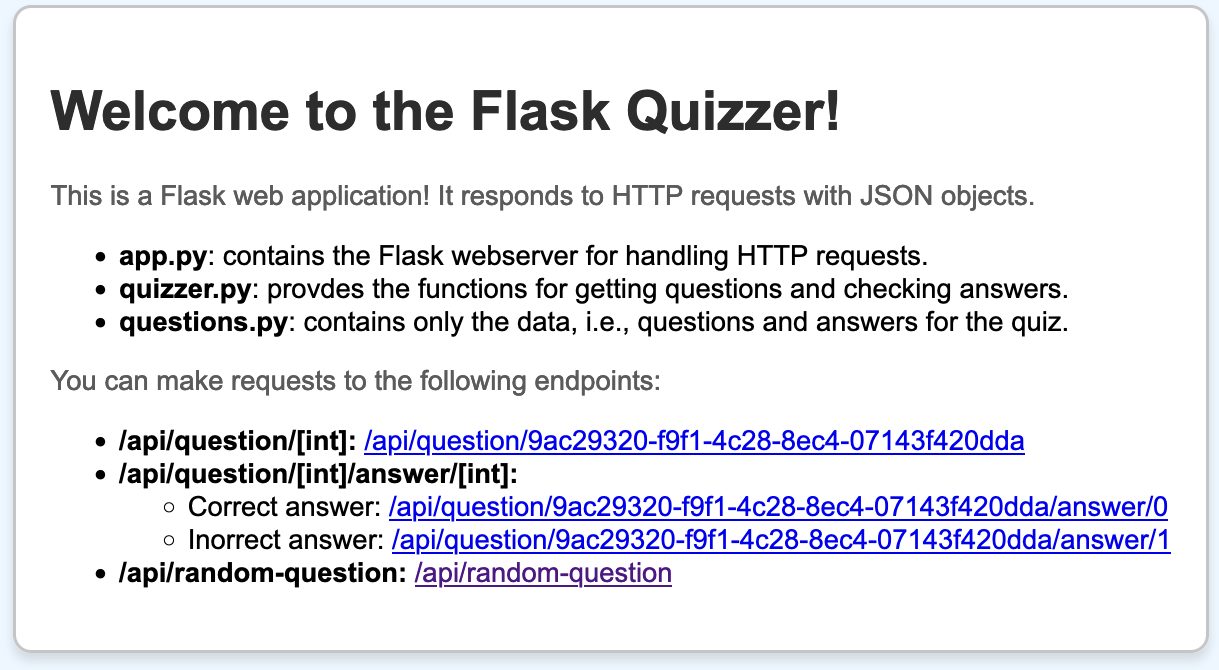
Great! You are now running a web application built in Python using the Flask library.
Interacting with the web app
Your web browser is a client and the Flask app is a server. Web browsers issue HTTP requests to servers, and the servers send an HTTP response.
Think of HTTP requests and responses as another envelope. The envelope is a merely a string of text in a particular format. The contents of the envelope are bits that can be strings, images, videos, audio, integers, floats, etc.
This Flask web app is sending its contents as strings in JSON format. The JSON form is very similar to a Python dictionary: it has keys and values.
Key commands
Make sure you have the project open in Visual Studio code and are using the Integrated Terminal.
- To start:
flask --app app run --debug - To stop: Hit
CTRL+Cwith the Terminal selected.