This lab provides the minimum introduction to PyCharm needed to write programs. PyCharm has similar functionality to other professional IDEs, such as Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ, or XCode.
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
04. PyCharm basics
1 - Keyboard shortcuts
Keyboard shortcuts
Everything you can do with a menu and a mouse has a keyboard shortcut. Menu+mouse is easier to learn, but keyboard shortcuts will make you about 30% more productive once you master them.
Rule of thumb: If you use the same mouse+menu commands over and over, learn the keyboard shortcut instead. Try to learn a shortcut or two each week.
I’ve highlighted my most-used keyboard shortcuts in the official cheatsheets from PyCharm:
2 - Managing files
Organizing and opening projects
The last thing we did in Installing the PyCharm IDE was to open the pycharm-test directory in PyCharm.
Rule #1: Keep each project, assignment, and lab in its own directory. This is the structure you want:
~/seng-201
├── assignment1
├── assignment2
├── lab01
├── lab02
└── pycharm-test
├── fib.py
├── hello.py
└── hello2.py- I have created a
seng-201/subdirectory in my home directory symbolized by the~. The tilde (~) is understood by your Terminal to mean “the current user’s home directory”. - Inside
seng-201/, I have created subdirectories for each project.
Rule #2: Open the specific project directory in PyCharm, not the parent directory. Suppose you want to work on assignment1, then you need to open the assignment1/ directory. You open a folder in PyCharm in two ways:
- Use your Terminal/CLI to
cdinto the project folder, then type (Windows)pycharm64 .or (Mac)pycharm .. Note that the.is important. - Open PyCharm first, then do
File → Open. Select the project directory, then clickOK.
The folder you open serves as the working directory for PyCharm. Do not open the parent directory, seng-201/, as it may create challenges running the Python code in the various subdirectories.
Project pane
The Project pane is where you browse and manage files. Open it by clicking on the foldier icon in the left sidebar:
Things you can do here include:
- Create new files and subdirectories.
- Double-click files to open.
- Right click files and directories for a variety of tools, like renaming and deleting.
Exercise
- Click on the
pycharm-testname. You created this folder when following the labs to install PyCharm. - Now right-click the directory name, then
New → Python File. Give it a name likefoo.py.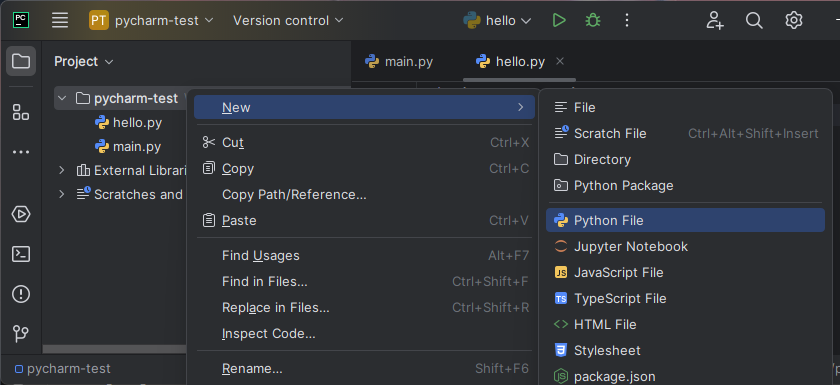
- You will see an editor tab pop open on the right with the name
foo.pyat the top.
Knowledge check:
- Question: (True/False) Each coding project should have its own directory on the filesystem?
- Question: (True/False) It’s okay to open the parent directory holding multiple projects in PyCharm?
- Question: What CLI command do you run to open PyCharm from the current directory?
3 - Editing code
Editing
An Editor pane will automatically open every time you open a file. Things to know about the Editor windows:
PyCharm automatically saves your files. No need to explicitly save.
The line numbers on the left side are used to identify individual lines of code in error messages and elsewhere.
Familiar text editing features like Cut and Paste are available in the
Editmenu at the top or Right-Clicking in an editor window. Learn those keyboard shortcuts!CMD+/(Mac) orCtrl+/(Windows, Linux) toggles comments on the current line or selected lines. This is one of my favorite keyboard shortcuts!Suppose your code calls a function defined elsewhere. Hold down
Cmd(Mac) orCtrl(Windows, Linux) and hover over the function call. It will turn blue like a link. Left click the link and the function definition in the editor. Very handy! Look up the Go back keyboard shortcut to return your cursor to where you were.Not happy with a variable or function name?
Right-click it > Rename...It will be renamed everywhere in scope!Use the arrow keys to move the cursor one character at a time. Hold down
Ctrl(Windows, Linux) orOption(Mac) while tapping the left- or right-arrows. You will skip entire “words”. Again, very handy. Hold downShiftas well to select those words!
Exercise
Create a new file called fib.py in your pycharm-test folder and paste in the following code:
def fibonacci(n):
"""
Computes and returns the Fibonacci sequence of length n.
Assumes n >= 1
"""
if n == 1:
return [1]
if n == 2:
return [1, 1]
result = [1, 1]
for i in range(2,n):
result.append(result[i-1] + result[i-2])
return result
print(fibonacci(1))
print(fibonacci(2))
print(fibonacci(6))
print(fibonacci(10))
- Hold down
Cmd(Mac) orCtrl(Windows, Linux) and mouse over one of thefibonacci()calls at the bottom. Click the link and watch the cursor jump. - Using the keyboard shortcut, comment out the first three
print(...)calls at the bottom all at once. - Now uncomment them all at once.
Right-clickafibonnaci()call and rename the symbol. Where does it change in the code?- Hit
Ctrl+ZorCmd+Zto undo the rename.
Knowledge check:
- Question: How do you comment/uncomment a block of code with your keyboard?
- Question: What does holding down
CmdorCtrl+ left-clicking on a name in the editor window do? - Exercise: Add a second function to your
fib.pyfile namedhello()that simply printsHello Worldwhen called. Now, try to rename (as described above) thehellofunction tofibonacci, which already exists. Describe what happens.
4 - Running code and the integrated terminal
PyCharm uses tools installed on your computer to run programs. PyCharm should automatically find the Python you have installed on your computer if installed in a “standard” location.
Running code
There are multiple ways to run a program file:
- In the editor window,
Right-clickanywhere in the code to open the context menu, then selectRun [filename]orDebug [filename].- If necessary, select the
Python Debuggerpopup, and select default options of subsequent pop-ups until you see the program run in the interactive Terminal at the bottom. - We will discuss the difference between
Debugand plainRunin the future.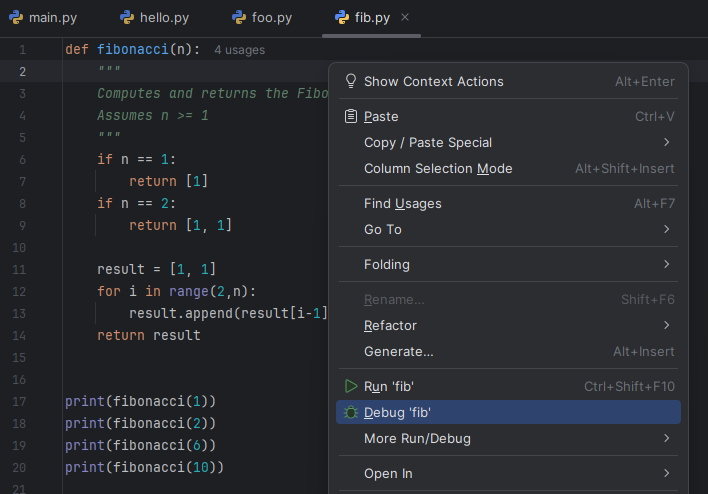
- If necessary, select the
- Use the run shortcuts at the top of the PyCharm window. You select the file you want to run from the dropdown, and then either the Run or Debug button. By default, PyCharm will run the most recent program run.
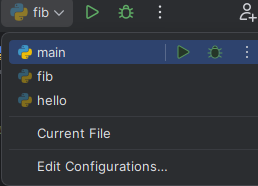
- Use keyboard shortcuts to re-run the most recent program:
Shift+F9(Windows, Linux) or^D(Mac) to DebugShift+F10(Windows, Linux) or^R(Mac) to Run without debugging.
Exercise
- Create
hello.pyin thepycharm-testdirectory if needed and addprint("Hello World") - Run
hello.pyusing the the context window. - Run it using the PyCharm toolbar.
- Run it using keyboard shortcuts.
When you run your hello.py program, you should see output in the Debug or Run pane at the bottom. The exact output differ from mine, but you should see Hello World in there.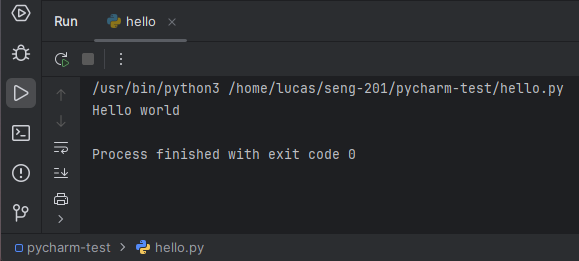
The Integrated Terminal
PyCharm also has an Integrated Terminal, which is an embedded version of the Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac). You can use CLI commands like cd, ls, mkdir, etc.
Open the Integrated Terminal by either:
- Clicking the Terminal icon in the bottom left
- Using the PyCharm menu,
View → Tool Windows → Terminal - Using the keyboard shortcut
Alt+F12(Windows, Linux) orOption+F12(Mac)
When you ran your hello.py program, you should have seen a flurry of output in the Integrated Terminal window at the bottom. What just happened?
- PyCharm opened a Terminal CLI, like you did in the Launching a Terminal lab, except this one is embedded in PyCharm.
- PyCharm issued the CLI command
pythonwith your file as an argument. pythonruns in the Terminal and prints output.
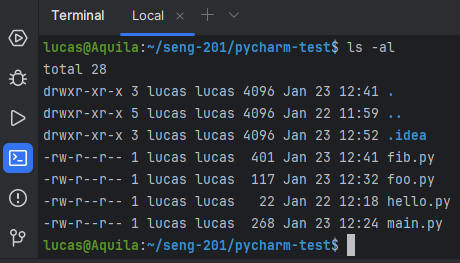
I find it convenient to use this integrated Terminal rather than switching to a another window. Or you may prefer to keep them separate. Do what works for you.
Exercise
- List directory contents in the integrated Terminal using the
lscommand. - Type
cd ~in the integrated Terminal to switch to your home directory. Notice how the contents of the Project pane do not change. You are only changing the working directory in the Terminal. - Use the Terminal to navigate to your
pycharm-testdirectory usingcdcommands. - Run the command
touch hello2.py. Does it appear in the Explorer pane? - Run the command
rm hello2.py. What happened? What happened in the Project pane?
Knowledge check:
- Question: What is the keyboard shortcut for debugging/running your program?
- Question: How do you open the integrated Terminal in PyCharm?
- Question: How can you print the name of the current working directory in the integrated Terminal?
- Question: If you have a runaway process in the integrated Terminal, how do you cancel/kill it so that you regain control of the Terminal? (The answer is the same as for the regular Terminal.)