Running code and the integrated terminal
PyCharm uses tools installed on your computer to run programs. PyCharm should automatically find the Python you have installed on your computer if installed in a “standard” location.
Running code
There are multiple ways to run a program file:
- In the editor window,
Right-clickanywhere in the code to open the context menu, then selectRun [filename]orDebug [filename].- If necessary, select the
Python Debuggerpopup, and select default options of subsequent pop-ups until you see the program run in the interactive Terminal at the bottom. - We will discuss the difference between
Debugand plainRunin the future.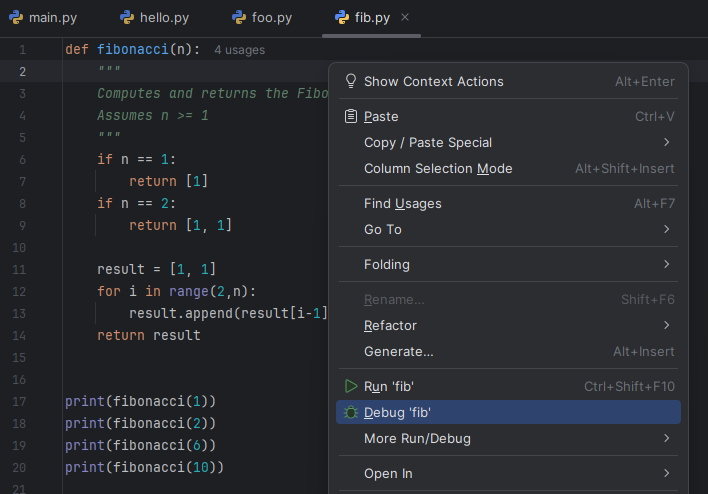
- If necessary, select the
- Use the run shortcuts at the top of the PyCharm window. You select the file you want to run from the dropdown, and then either the Run or Debug button. By default, PyCharm will run the most recent program run.
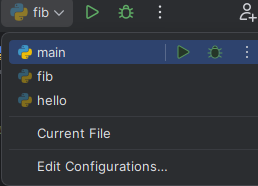
- Use keyboard shortcuts to re-run the most recent program:
Shift+F9(Windows, Linux) or^D(Mac) to DebugShift+F10(Windows, Linux) or^R(Mac) to Run without debugging.
Exercise
- Create
hello.pyin thepycharm-testdirectory if needed and addprint("Hello World") - Run
hello.pyusing the the context window. - Run it using the PyCharm toolbar.
- Run it using keyboard shortcuts.
When you run your hello.py program, you should see output in the Debug or Run pane at the bottom. The exact output differ from mine, but you should see Hello World in there.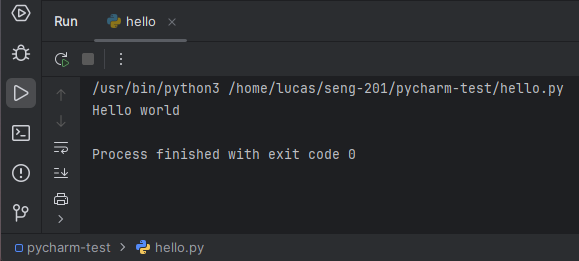
The Integrated Terminal
PyCharm also has an Integrated Terminal, which is an embedded version of the Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac). You can use CLI commands like cd, ls, mkdir, etc.
Open the Integrated Terminal by either:
- Clicking the Terminal icon in the bottom left
- Using the PyCharm menu,
View → Tool Windows → Terminal - Using the keyboard shortcut
Alt+F12(Windows, Linux) orOption+F12(Mac)
When you ran your hello.py program, you should have seen a flurry of output in the Integrated Terminal window at the bottom. What just happened?
- PyCharm opened a Terminal CLI, like you did in the Launching a Terminal lab, except this one is embedded in PyCharm.
- PyCharm issued the CLI command
pythonwith your file as an argument. pythonruns in the Terminal and prints output.
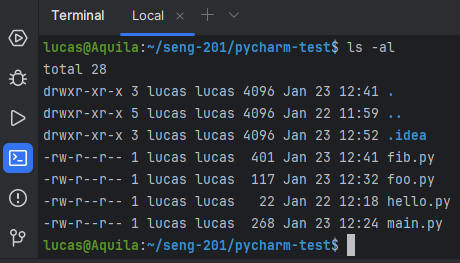
I find it convenient to use this integrated Terminal rather than switching to a another window. Or you may prefer to keep them separate. Do what works for you.
Exercise
- List directory contents in the integrated Terminal using the
lscommand. - Type
cd ~in the integrated Terminal to switch to your home directory. Notice how the contents of the Project pane do not change. You are only changing the working directory in the Terminal. - Use the Terminal to navigate to your
pycharm-testdirectory usingcdcommands. - Run the command
touch hello2.py. Does it appear in the Explorer pane? - Run the command
rm hello2.py. What happened? What happened in the Project pane?
Knowledge check:
- Question: What is the keyboard shortcut for debugging/running your program?
- Question: How do you open the integrated Terminal in PyCharm?
- Question: How can you print the name of the current working directory in the integrated Terminal?
- Question: If you have a runaway process in the integrated Terminal, how do you cancel/kill it so that you regain control of the Terminal? (The answer is the same as for the regular Terminal.)