Quiz 2
Study guide and sample long-form problems for Quiz 2.
Format and Rules
- The quiz is in class, Thursday, October 2.
- A mix of multiple choice, fill-in-the-blank, and long answer questions.
- You will not be programming in PyCharm, but you may be asked to write or edit code snippets by hand.
- You may bring 1 side of 1 sheet of letter paper with your own hand-written notes.
- An Honor Code violation on any quiz or exam results in a course grade of F.
- Failure to submit a quiz or exam results in a course grade of F.
Content
- Study key terms from slides and labs. Look for boldfaced, underlined terms in slides and emphasized terms in labs.
- Study Knowledge Checks from labs.
- Writing a good Problem Statement when provided a high-level description of the program goals. (week 4)
- Testing concepts (terms) and application (weeks 4-6), including:
- Creating a control flow graph for a given function and identifying all unique program paths.
- Writing or analyzing unit tests for a given function, including:
assertstatements- testing if exceptions are raised using
pytestfunctions - writing tests that cover all unique program paths from a CFG.
Sample CFG and Testing problems
You will be asked to draw CFGs and write test cases that cover all program paths.
Disclaimer: You will have other knowledge check questions beyond these types of questions.
Sample 1
| |
- Draw the CFG for this code using the conventions from class.
- List the unique program paths.
- Add
assertstatements to the following test case that exercise all unique program paths.def test_is_prime(): # Your code here.
Solution
CFG for is_prime()
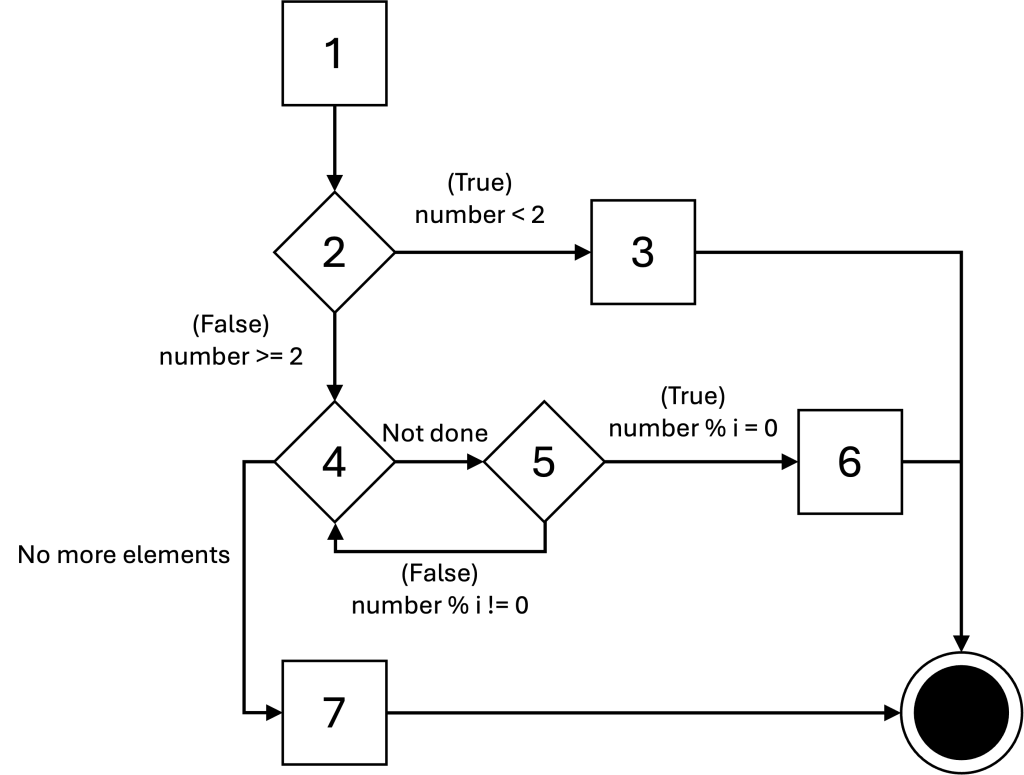
unique program paths
The unique edges in the path are highlighted. You do not need to highlight the unique edges on the quiz.
- (1, 2, 3)
- (1, 2, 4, 7)
- (1, 2, 4, 5, 6)
- (1, 2, 4, 5, 4, 7) or (1, 2, 4, 5, 4, 5, 6)
test case
def test_is_prime():
# Some paths can be exercised with multiple input values.
# The goal is to exercise all program paths.
assert is_prime(1) == True # tests path (1, 2, 3)
assert is_prime(2) == True # path (1, 2, 4, 7)
assert is_prime(4) == False # path (1, 2, 4, 5, 6)
assert is_prime(5) == True # path (1, 2, 4, 5, 4, 7)
Sample 2
| |
- Draw the CFG for this code using the conventions from class.
- List the unique program paths.
- Add
assertstatements to the following test case that exercise all unique program paths.def test_generate_fibonacci(): # Your code here.
Solution
CFG for generate_fibonacci()
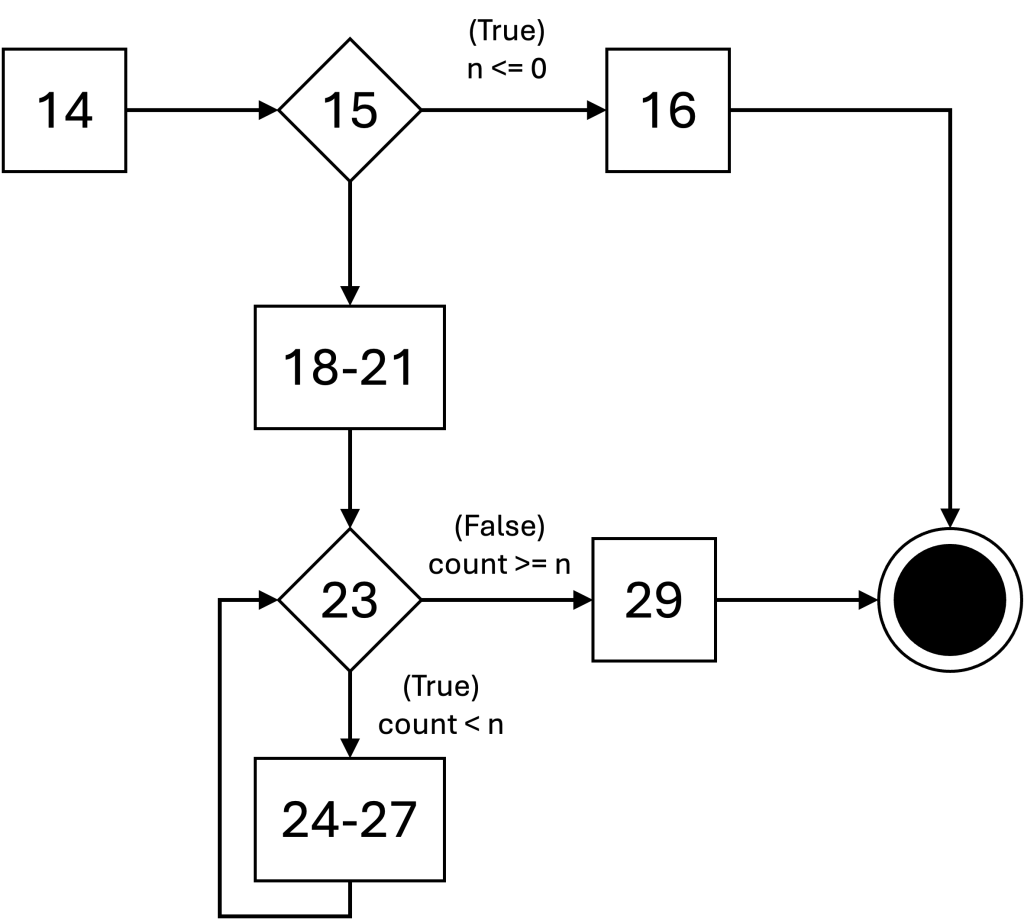
unique program paths
The unique edges in the path are highlighted. You do not need to highlight the unique edges on the quiz.
- (14, 15, 16)
- (14, 15, 18-21, 23, 29)
- (14, 15, 18-21, 23, 24-27, 23, 29)
test case
def test_generate_fibonnaci():
# Some paths can be exercised with multiple input values.
# The goal is to exercise all program paths.
assert generate_fibonnaci(0) == "Error: Number of terms must be a positive integer" # tests path (14, 15, 16)
assert generate_fibonnaci(1) == [1] # path (14, 15, 18-21, 23, 29)
assert generate_fibonnaci(6) == [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8] # path (14, 15, 18-21, 23, 24-27, 23, 29)
Sample 3
| |
- Draw the CFG for this code using the conventions from class.
- List the unique program paths.
- Add
assertstatements to the following test case that exercise all unique program paths.def test_factorial(): # Your code here.
Solution
CFG for factorial()
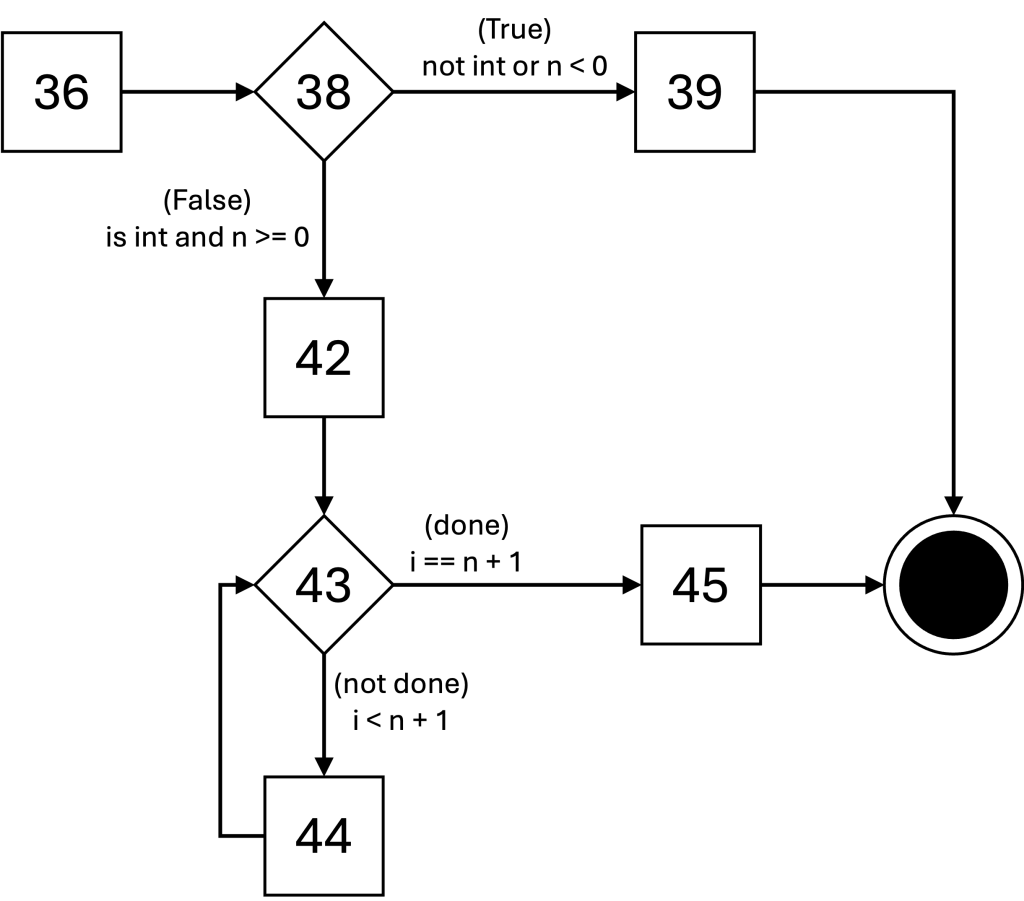
unique program paths
The unique edges in the path are highlighted. You do not need to highlight the unique edges on the quiz.
- (36, 38, 39)
- (36, 38, 42, 43, 45)
- (36, 38, 42, 43, 44, 43, 45)
test case
def test_factorial():
# Some paths can be exercised with multiple input values.
# The goal is to exercise all program paths.
assert factorial("Alice") == "Error: Number of terms must be a positive integer" # tests path(36, 38, 39)
assert factorial(-1) == "Error: Number of terms must be a positive integer" # also tests path(36, 38, 39)
assert factorial(0) == 1 # tests path(36, 38, 42, 43, 45)
assert factorial(5) == 120 # tests path(36, 38, 42, 43, 44, 43, 45)